
SECOND EPISODE
had spent ten days from the interview that we reported. One evening about eight o'clock, a group of ten people was started, chatting to the house of Cavalier Prosdocimo. Who wanted to push his curiosity to know the members of the group, would have noticed at the forefront of the source Pasquale, who is waving a clay importance, Sor Lorenzo, local master, Sor Antonio, conciliator from time immemorial, appears Cecco - that of phylloxera - , Sor Andrea, postmaster, postmaster and owner of vineyards, three or four other good wine of the country, young and old, and finally, amid all the Provost: a good country priest, who cared not only to the souls entrusted to him, but also the land of the prebend.
At eight and a half, everyone was gathered around a large table in the dining room of the Knight. A fire spread around the warmth and joy of a beautiful flame, a dusty bottle in the middle of the table once said that the brigade was not friendly .... antialcoolica. After the first talk of circumstance and a glass of wine introduction, the cav. Prosdocimo began:
If we want to be clear right from the outset, we agree to start our conversations from a first point, that maybe you seem a bit 'hard, and perhaps even necessary, and that I will know it is absolutely necessary: \u200b\u200bI want to allude to the knowledge of life not as culture but as a plant. A professor would say, must begin with the botany of the screw. I must say that I will be shorter and simpler than is possible. And I urge you not to be scared in this first evening I'll pull holes of the words a bit 'difficult: it takes patience, and we must accept them as they are. The screw, therefore, belongs to a family of plants, which botanists have named Ampelidee. Of these plants, many are of no importance for us then we will not describe, while others concern us very closely. The latter are the so-called species of the genus Vitis (not exposed to some little 'in Latin!).

One of these species is called by botanists Vitis vinifera. Take my hat off to it, because this is precisely the vines grown by us from time immemorial, in Italy and other countries in Europe. Tuttee the wine varieties that you know, that were already cultivated by our older son all of the varieties of Vitis vinifera or European lives. In addition to this European vines, there are several other species of vines: some of them American, other Asian countries. Among the former, we find the screws that have great importance for us today: namely, to protect us from the disasters of phylloxera. And that is what we should know at least the main among them. But for now let's move on. Those of you who wish to know the names of the various species of the genus Vitis, can be seen later with his convenience, here against the picture, where you will find all the names of these species, and regions where they live in their natural state. Let
then to look a bit 'close the screw in general is to understand a bit' about its various parts or organs. Let's start with roots in the screws, as in any crop, there is first the root, which normally is in the ground. If we look at this root, we see, thick and woody at the soil surface, it is becoming more subtle and delicate as it deepens and moves away from the strain. That brings us to the last branch of it, equipped with thin hair, said just root hairs. Mind you that these sprouts thinner hairs are equipped with the most important for plant nutrition. This fact does not absorb food already with the thickest part of the root, but with those tiny Barbolini. This is good to remember always, everything we say below. A special note is good right now, about the roots, is this: if you look like you have roots in various species of vines, you find significant differences.
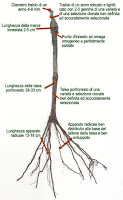
differences not only development, which can be larger or smaller, but very sensitive to differences in provision, specifically in the secondary or lateral roots that form with the principal or the vertical line. In some species, these roots are lateral to the vertical angle too wide, in others very narrow. This has its importance, because the screws have this angle (called geotropic) very large, they suffer far more than the droughts that have very narrow. The stem The root is still in the barrel, which is usually above ground. Frame is also present in the screw size and can look very different. However, we will call the log part of it is larger and closer to the ground; branches in parts where the strain is divided, the branches the branches of a year who are placed on the branches, shoots the last term, yet the grass stem. If we look at a branch, we see that it is divided into many portions of some swelling, which are the nodes, the same portions are called internodes or meritalli. If you split Pearl length of a branch, has found that outside the bark, below this wood, in a spring that is part of the bone. However, this bone is interrupted at the nodes, leaving a portion hard, woody, said diaphragm.

LE then you see some buds on the nodes corpiccioli, conical in shape, which are the gems, or as you call them, the eyes. Should we do about it some distinction. Most of these gems will not open and not to vegetate the following spring: they are the so-called dormant buds, and are the most important. See that you see on a node distinctly one dormant bud; is the main bud, but beyond it there are other, hidden, that do not open it in case it is destroyed the seed of the gem main are the gems of replacement or contr'occhio. In addition to these dormant buds, the buds, however, we are ready. This has the ability to grow in the same hatch where they are formed, giving a spear, called Femminella, which is mostly useless to us. Finally we must remember that on the stump and branches are located, hidden by the bark, here and other gems, which grow only in certain cases: there are the so-called latent buds, and shoots that sprout from them are called suckers or bastards , and feature almost always be non-interest bearing.

THE LEAF Always on the nodes of the branches are part of the leaves. These are important organs for the vine, because, along with the roots, they think the nurturing of the plant. Much could be said about them, but we will limit ourselves to a few words. As you know the leaves of the vine have a stem or stalk, which can be shorter or longer, and a sheet or strip, which can be very different in shape or size. It is sometimes nearly round, entire or, more often has some nicks in outline, those breasts, and then is divided into several sections, called lobes. If these three, the leaf is said troubled, and if there are five five-lobed. The breasts are then less open or closed: Very interesting in this regard is the attack which is found within the stalk (petiole sinus). A character of the leaf that care must be taken is the presence or absence of hair on its underside. If there are no hair at all, decided the leaf glabrous. If there are few, it is said pubescent; though many tomentosa. I said that the leaf is of great importance for plant nutrition. In fact, it does three different jobs: it breathes, like other parts of the plants, like animals and like us, breathes, that gives out the excess water content in the plant, a body that absorbs carbon, it removes a gas content in the air, which is called, "Carbon dioxide". This work, which is precisely what it takes to plant nutrition, the leaves do not, however, that sunlight and a temperature high enough. CIRRs Other organs of the lives that are placed on the nodes of the branches, but opposed to the leaves, are cirrus or tendril. Are these the kind of filaments, which winds around to support any, help the screw to keeping the high ground from various parts of his trunk, which would not have sufficient strength to stand by itself. In the same position occupied by the cirrus clouds, ie the nodes, as opposed to the leaves, the clusters are found. When I say clusters, we refer to the flowers or fruits. We start two words refer to the flowers.

the flowers in life, the flowers are found together in large numbers, drawn from n branched axis, and together constitute exactly the bunch. Each flower vine has the following parts: the outside is like a tiny cup of green glass that is formed by five small sepals. Inside the cup is found, the corolla, composed of five petals, pure green. When the flower is still closed, it is a kind of cap, because the petals are welded at the top. But when the flower is mature, these petals are wrapped up on themselves and the corolla falls. Then appear five strands terminating in a sort of heads: they are the stamens or male organs with the anthers. They contain a yellow powder is pollen, or male element. Among the stamens is found a green body, which is somewhat reminiscent of the form 'a pear or a failure: it is the pistil or female organ with a lower part called the ovary, containing mostly four eggs, a median, which is the stylus, a higher is the stigma. Ova fertilized by pollen, become seeds, while the ovary becomes the fruit. It 'important to note that usually the pollen of one flower fertilizes the ovary is not the same flower. For the most part lives in the cross-fertilization, ie, the pollen of a screw, transported by wind or insects, is to fertilize the pistils of another. And yet I must add that the flowers do not always have all parts of life that I have appointed. We have flowers without pistils: the so-called male flowers. They contain the pollen that can fertilize other flowers, but they will never turn into fruit, the absence of the female organ. Finally, we may find the female flowers in which stamens exist, but instead of being long and straight, are short and turned down. The pollen of these stamens is much less fertile than that of ordinary flowers (hermaphrodite), and is therefore more than one case in which fruiting in these screws is less secure than in the common screw.

dried fruit to the fruit. I said that the ovaries become fertilized fruits. You know that these are in the vine of grapes or berries, in clusters. These can be large or small, tight or sparse (ie, the grapes from each other), cylindrical, pyramidal, simple or winged (ie, the Grappolini side by side with the main one). The berries possonopoi be of different sizes, round, round sub (ie not just round), oval or elongated ellipsoids. The skin may be more or less thick, covered more or less abundant than that powder cinerea, which is said to bloom. Inside, the berry contains a more or less fleshy pulp or dissolved, which are located in the middle of the seed or seeds. SEEDS The seeds, or seeds, they would normally be four, but one of them is often aborted. Sometimes miss them: then the berries are said to be seedless. Each grape has a shape of a small pear, with a pointed end, which is said spout, a depression on the back that is called chalazion, a cord running from this chalazion and goes to end on ventral side, which is called the raphe. Inside the seeds contain a rich oily substance content, which will serve for food at the tender seedling when the seeds germinate. This map is an essential part of originerà from seed that is the embryo.
And with that, my friends, concluded the cav. Prosdocimo, we have had a look, albeit interim, but certainly a bit 'more careful of what you usually do not do, so we are interested in the plant. For tonight just because you do not want to start with ... .. indigestion. A good bye, then, and good night!
0 comments:
Post a Comment